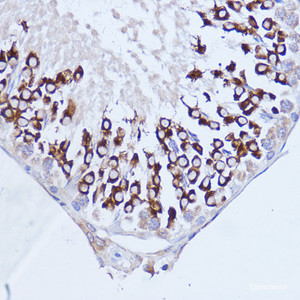
PTPRM Polyclonal Antibody | G-AB-02929
Gentaur Antibodies
- SKU:
- G-AB-02929
- Availability:
- 3 to 5 Working Days
- Host:
- Rabbit
- Reactivity:
- Human, Mouse
PTPRM Polyclonal Antibody | G-AB-02929 | Gentaur Antibodies
Overview: The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and two tandem catalytic domains, and thus represents a receptor-type PTP. The extracellular region contains a meprin-A5 antigen-PTP mu (MAM) domain, an Ig-like domain and four fibronectin type III-like repeats. This PTP has been shown to mediate cell-cell aggregation through the interaction with another molecule of this PTP on an adjacent cell. This PTP can interact with scaffolding protein RACK1/GNB2L1, whicHuman, Mouseay be necessary for the downstream signaling in response to cell-cell adhesion. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcripts encoding distinct isoforms.
Category Type: Polyclonal Antibody
Research Areas: Signal Transduction
Synonyms: hR PTPu, Protein tyrosine phosphatase mu, Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type M, Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type mu polypeptide, Protein-tyrosine phosphatase mu, PTPRL1, Ptprm, PTPRM, R PTP mu, R-PTP-mu, Receptor type tyrosine protein phosphatase mu, Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase mu, RPTPM, RPTPU
Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Host: Rabbit
Isotype: IgG
Gene ID:
Accession #: NP_002836
Clonality: Polyclonal
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide of human PTPRM
Clone #:
Conjugation: Unconjugated
Swissprot: P28827
Santa Cruz: sc-1115/sc-25433
Calculated MW:
Observed MW:
Concentration: 1.1 mg/mL
Buffer: PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, PH7.4
Purification method: Affinity purification
Application: IHC, ELISA
Dilution: IHC 1:100-1:300
Storage: Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.