DMRT3 Polyclonal Antibody | G-AB-00958
Gentaur Antibodies
- SKU:
- G-AB-00958
- Availability:
- 3 to 5 Working Days
- Host:
- Rabbit
- Reactivity:
- Human, Mouse, Rat
DMRT3 Polyclonal Antibody | G-AB-00958 | Gentaur Antibodies
Overview: The DMRT (doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor) genes encode a large family of transcription factors that are related to the Drosophila doublesex proteins. Expressed primarily in the gonads, DMRT proteins contain cysteine-rich DNA-binding motifs and are thought to play an important role in sexual development. DMRT3 (doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 3) , also known as DMRTA3, is a 472 amino acid protein that contains one DM DNA-binding domain and belongs to the DMRT family. Localized to the nucleus, DMRT3 is expressed specifically in testis and is thought to regulate transcriptional events during early sexual development. The gene encoding DMRT3 maps to human chromosome 9, which houses over 900 genes and comprises nearly 4% of the human genome. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, which is characterized by harmful vascular defects, and Familial dysautonomia, are both associated with chromosome 9. Notably, chromosome 9 encompasses the largest interferon family gene cluster.
Category Type: Polyclonal Antibody
Research Areas: Cancer, Metabolism, Developmental Biology
Synonyms: DMRT 3, DMRT like family A3, dmrt3, DMRT3, DMRTA3, Doublesex and mab 3 related transcription factor 3, Doublesex- and mab-3-related transcription factor 3, MGC142144, Testis specific protein
Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
Host: Rabbit
Isotype: IgG
Gene ID:
Accession #: BC113584
Clonality: Polyclonal
Immunogen: Recombinant protein of human DMRT3
Clone #:
Conjugation: Unconjugated
Swissprot: Q9NQL9
Santa Cruz: sc-82581/sc-82580/sc-82579
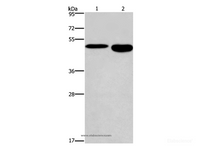
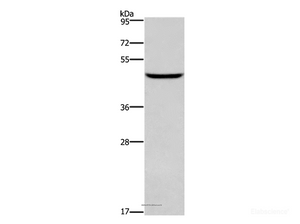
Calculated MW: 51 kDa
Observed MW:
Concentration: 0.4 mg/mL
Buffer: PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, PH7.4
Purification method: Affinity purification
Application: WB, ELISA
Dilution: WB 1:500-1:2000
Storage: Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.